Species Index

Key Facts
Length: Up to 2.7 metresRange: Tropical waters
Threats: Entanglement in fishing gear, pollution
Diet: Variety of fish, squid and shrimp
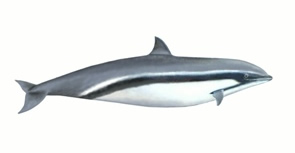
Fraser's Dolphin
Latin: Lagenodelphis hosei
Physical Description
Fraser’s dolphins are robust-bodied animals that can measure up to 2.7 metres in length. Most distinctive is the short beak, small dorsal and pectoral fins and small tail fluke. The back and dorsal fin are dark grey and the belly is paler in colour. A dark grey stripe runs from the melon to the anus. A second stripe runs from the mouth to the pectoral fins, which are also dark grey. The tip of the beak is commonly dark grey. This colour pattern can be highly variable among individuals.
Habitat and Distribution
Fraser’s dolphins are an oceanic species that inhabit deep tropical waters worldwide. They are extremely rare in UK waters. Sightings in the UK may suggest movements with warm ocean currents during the summer, which bring them further north than normally expected. There have been no live sightings of Fraser’s dolphin in the Hebrides, and one stranded animal.
Behaviour
Within their range, Fraser’s dolphins are known to form large groups of up to 1000 animals, but can also be seen in small groups of just a few dolphins. Fraser’s dolphins are not known for their aerial acrobatics but will occasionally bow ride boats for just a few minutes.
Food and Foraging
Fraser’s dolphins are known to feed on a variety of fish, shrimp and squid.
Status and Conservation
The main threat to Fraser’s dolphins is entanglement in fishing gear, although this is not thought to be significant. Small numbers are targeted in subsistence harpoon hunts in Indonesia and the Philippines. They are also threatened by pollution in their natural environment including chemical toxins, in addition to disturbance from boat traffic and noise. Fraser’s dolphins are protected under UK and EU law, principally under Schedule 5 of the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981, the Nature Conservation (Scotland) Act 2004 and by the 1992 EU Habitats and Species Directive.





